Mastering 3D Scanning for Printing: A Comprehensive Guide to Capturing Physical Objects
03/26/25
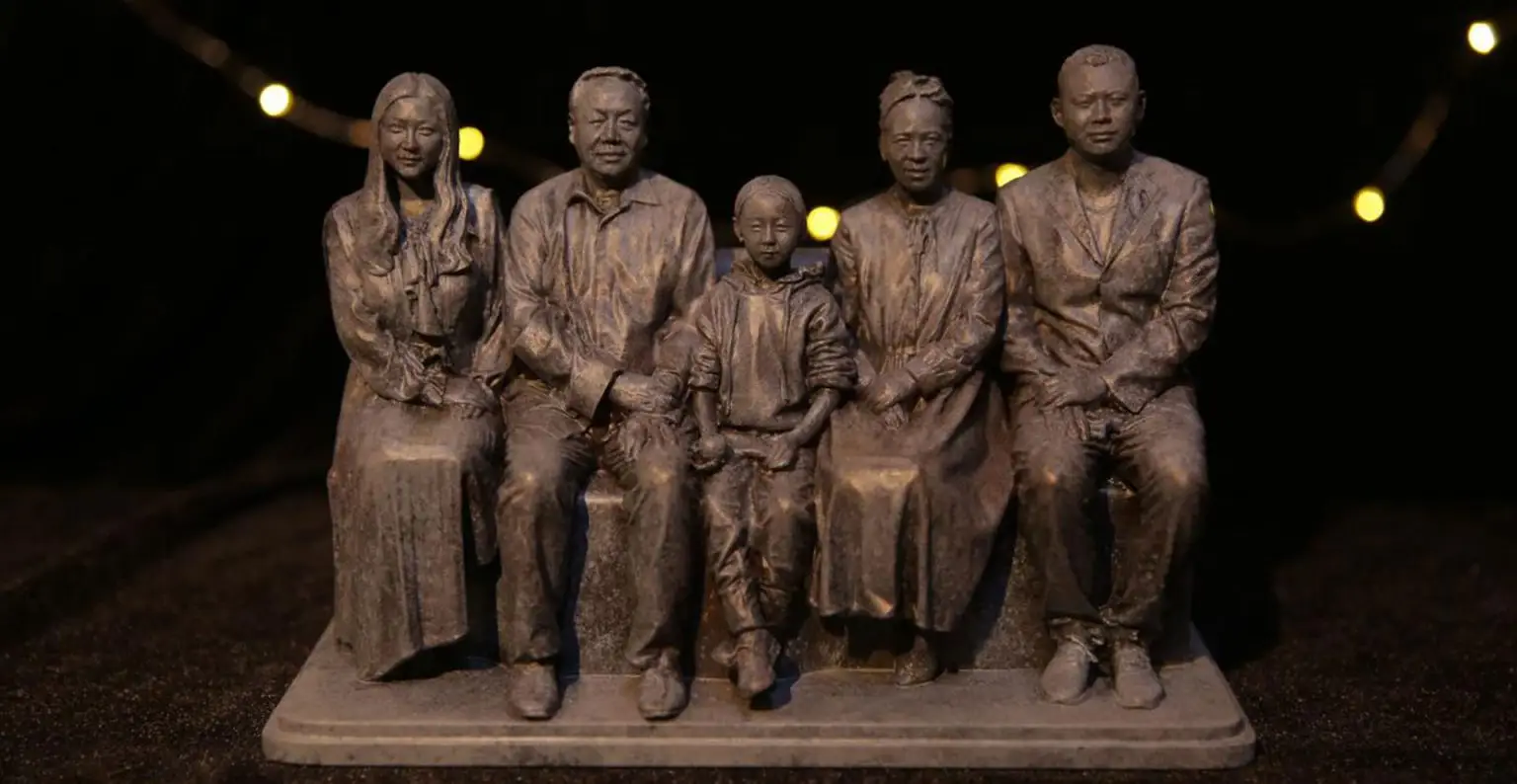
3D printing has revolutionized industries from manufacturing to healthcare, offering unique solutions for prototyping, part production, and even artistic design. However, the success of any 3D printing project begins before you even hit the “print” button. The key to ensuring that your printed object is accurate, functional, and visually precise starts with a high-quality scan. This step-by-step guide will help you understand the importance of accurate 3D scanning, how to choose the right 3D scanner for 3D printing, and how to prepare your scan for the printing process. Whether you’re an amateur hobbyist or a professional in the field, mastering the scanning process with a 3D scanner for 3D printing will unlock the full potential of 3D printing.
Understanding the Importance of Accurate Scanning for 3D Printing
At 3DeVOK, we understand that precision is at the heart of every successful 3D printing project. Without an accurate scan, your printed object could suffer from misalignments, poor resolution, or inaccuracies that affect its functionality and appearance. Therefore, taking the time to perform high-quality 3D scanning is essential.
Inaccurate scans often lead to errors in the printing process, resulting in wasted time, materials, and resources. For industries that rely on 3D printing for prototyping or production, these mistakes can be costly. Therefore, ensuring the quality of your scan is the first step toward achieving great results.
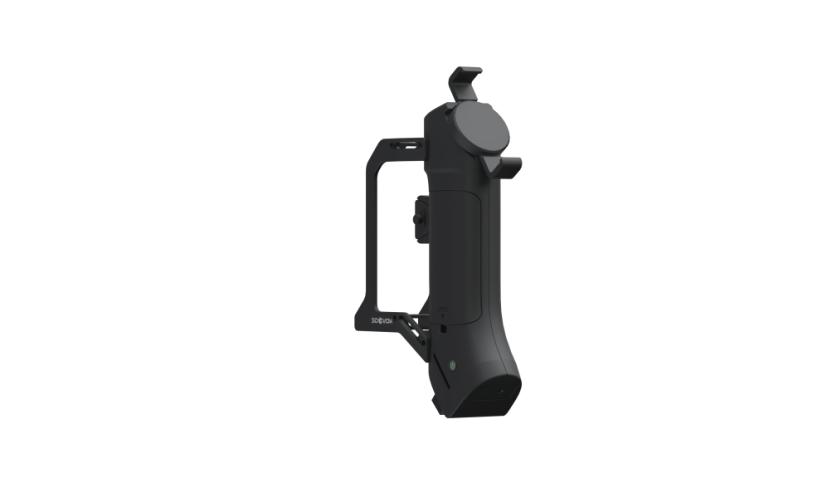
Choosing the Right 3D Scanner for the Job
When considering a 3D scanner, there are several factors to keep in mind. First, think about the level of detail required for your project. Some scanners are designed for larger, simpler objects, while others can capture the intricate details of smaller, more complex items.
At our company, we know that it’s important to choose a scanner that fits your specific needs. If you’re working on industrial-grade parts, you’ll want a high-resolution scanner that can capture fine details with accuracy. Additionally, the speed of the scanner and its ease of integration into your existing workflow are crucial considerations.
A good 3D scanner should also allow for flexibility, supporting various materials and scan sizes. Whether you need to scan objects for reverse engineering, quality control, or design purposes, choosing a versatile scanner can ensure smooth and efficient operations.
Processing the 3D Scan and Preparing for Printing
Once you’ve captured your 3D scan, the next step is processing the data to make sure it’s ready for printing. This involves importing the scan into compatible software where you can edit and refine it as needed. At our company, we often recommend tools that allow you to repair scan data, fill in holes, and optimize surfaces for a better print outcome.
The format of your scan plays an important role in this stage. Most 3D printers work with specific file formats such as STL or OBJ. Converting your scan into one of these formats is key to ensuring compatibility with your 3D printing software. It’s also important to ensure that your model has the right scale and proportion to avoid print errors.
Final preparation may involve checking for any errors in the scan that could affect the final output. This includes ensuring that no unwanted noise or distortions remain, which could create problems during printing. After these adjustments, your scan is ready to be sent to the printer for production.
Conclusion
By following these steps and investing in the right tools, such as a 3D scanner for 3D printing, you can ensure that your 3D printing projects start with the best possible foundation—a precise, high-quality scan. With the right scanner and the proper workflow, the entire process from scanning to printing can be smooth and efficient.
Related Articles
View Our Product